
| This tutorial will guide you through the main features of the FluSurver. 1) USER INPUT 2) RESULT SUMMARY 3) RESULT: BLAST ALIGNMENT 4) RESULT: SUMMARY OF MUTATION 5) MUTATION: Map of Global Distribution of Mutation 6) MUTATION: Global Statistics of Mutation 7) MUTATION: Table of occurrence of the mutation in other viral strains 8) MUTATION: Literature that described about the mutation or its equivalent site 9) MUTATION: Structural view of mutation and its interactions with ligands 10) MUTATION: Table of structures from Protein Data Bank showing ligand interacting at site of mutation 11) RESULT: STRUCTURAL VIEW OF MUTATIONS 12) RESULT: TABLE SUMMARY OF MUTATIONS 1) USER INPUT The homepage of the Flusurver looks like this: 
Sequence(s) could be pasted into the textbox, or uploaded in a file in fasta format. User may choose to allow the Flusurver to automatically compare their sequences to the closest reference strains or select from a dropdown list of reference strains to compare their sequence(s) against. A few additional settings could be selected at the checkboxes according to the user's requirements. There is also an option for user to select the server closest to their location at the bottom of the homepage. Back to Top 2) RESULT SUMMARY A graphical summary of the mutations found in the sequences entered by the user will be similar to the following: 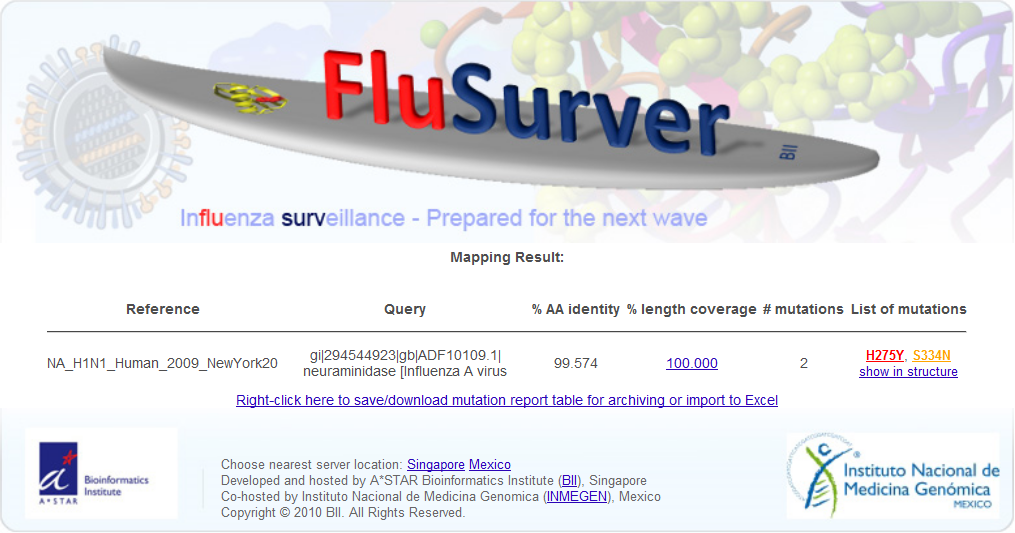
For each of the input sequences, there are six columns of information generated in the result summary page. From this Result Summary page, user may proceed to look at the query sequence's alignment to the reference strain (section 3), get more information on the mutation (section 4, which further extends to section 5-10), generate a structural view of all the mutations in the query sequence ("show in structure" section 11) or view a summary of the mutations in a table (section 12). The mutations are color-coded according to their known or predicted biological effects. When there are no known effects for the mutation, the mutation will appear in black colored font and assigned warnlevel 0 (least significant). When the mutation is a common subtype marker, the mutation will appear in green colored font and assigned warnlevel 0 (least significant). Mutations occurring at a site of interaction will appear in blue colored font and assigned warnlevel 1 (moderately significant). If the mutation occurs at a site known to involved in drug-binding or alters host-cell specificity, it will appear in orange and assigned warnlevel 2 (significant). Mutations will also appear in orange and assigned warnlevel 2 when its equivalent site is known to result in antigenic shifts or causes mild drug resistance. Only mutations that are known to alter the virulence of the virus, cause strong drug resistance or reverses the effects of the premature STOP codon in the PB1-F2 gene of pandemic H1N1 will appear in red and assigned warnlevel 3 (most significant). Back to Top 3) RESULT: BLAST ALIGNMENT The following blast alignment output will be displayed when user click on the % length coverage hyperlink in the Result Summary page. 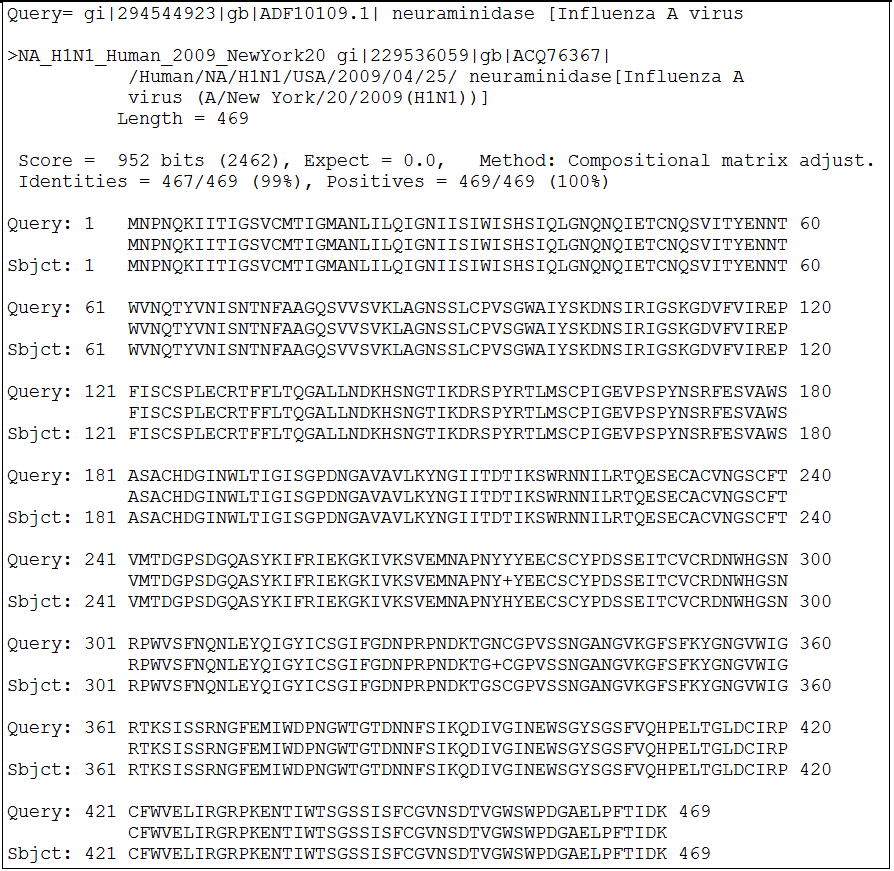
The alignment output enables the user to determine where in the query sequence differs from the reference sequence. Other changes such as a possible alteration to the N-linked asparagine glycosylation sites in the hemagglutinin or neuraminidase proteins could also be visually observed. Back to Result Summary Back to Top 4) RESULT: SUMMARY OF MUTATION The following summary page of a mutation will be displayed when user click on any of the mutation hyperlink in the Result Summary page. 
The Summary of Mutation page reports the global occurrence of the mutation based on sequences submitted to Genbank. A "Map of Global Distribution of Mutation" (section 5) will be generated when user click on the "see map" hyperlink. The "See detailed global statistics for this position" hyperlink will generate a window displaying a table similar to that seen in section 6. Hyperlinks that describes the effects of the mutation will generate a report detailing a brief summary of the information retrieved from the relevant literature (section 8). The hyperlink that describes interactions at the site of mutation in resolved structures will lead to an interactive jmol applet with the mutation highlighted (section 9). The "See all interactions for this position" hyperlink generates a table of all resolved structures with interaction at the site of mutation (section 10). Back to Result Summary Back to Top 5) MUTATION: Map of Global Distribution of Mutation The following will be displayed when user click on the "see map" hyperlink in the Summary of Mutation page. 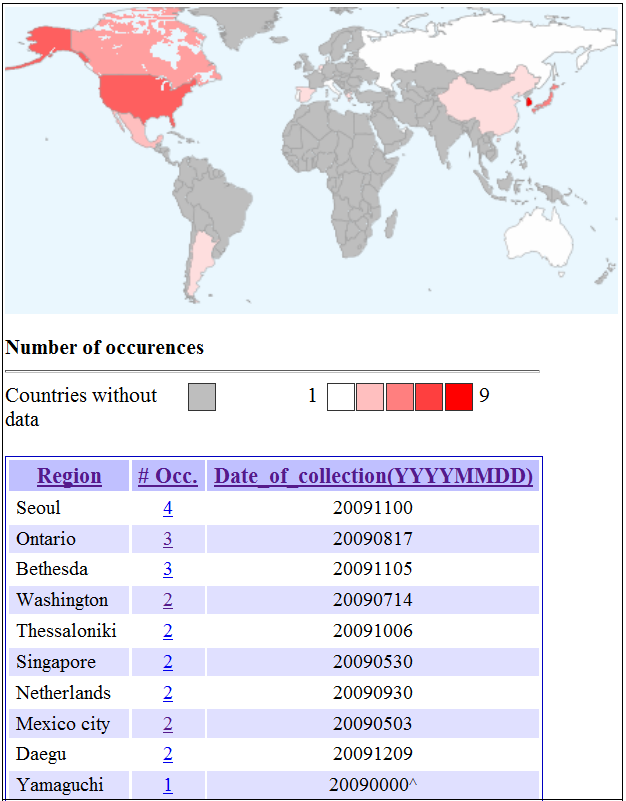
The map illustrates the distribution of the mutation in the globe based on sequences submitted to Genbank. The hyperlinks for the number of occurrences in each region will lead to the NCBI page where these sequences could be retrieved. The earliest date of collection of the viral samples are indicated and dates with a caret "^" at the suffix represents sequence that lacks complete date information. Back to Summary of Mutation Back to Top 6) MUTATION: Global Statistics of Mutation The following will be displayed when user click on the "See detailed global statistics for this position" hyperlink in the Summary of Mutation page. 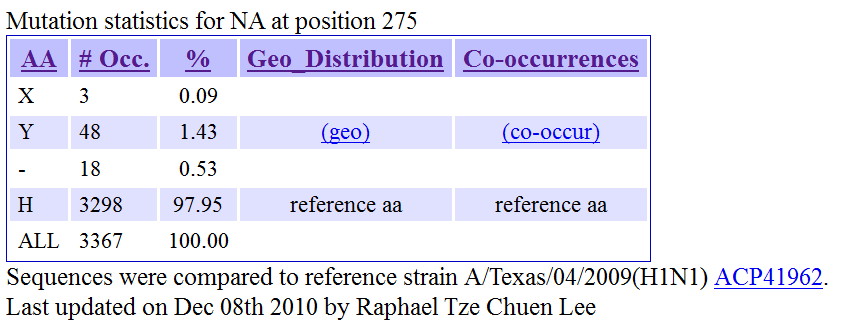
The statistics seen in this table are based on sequences submitted to Genbank. The "(geo)" hyperlink seen in this table of statistics will generate a map similar to that seen in section 5. The "(co-occur)" hyperlink on the other hand will generate a table of viral strains from Genbank containing this mutation together with mutations co-occurring with this mutation (section 7). Back to Summary of Mutation Back to Top 7) MUTATION: Table of occurrence of the mutation in other viral strains The following will be displayed when user click on the "(co-occur)" hyperlink in the Global Statistics of Mutation page. 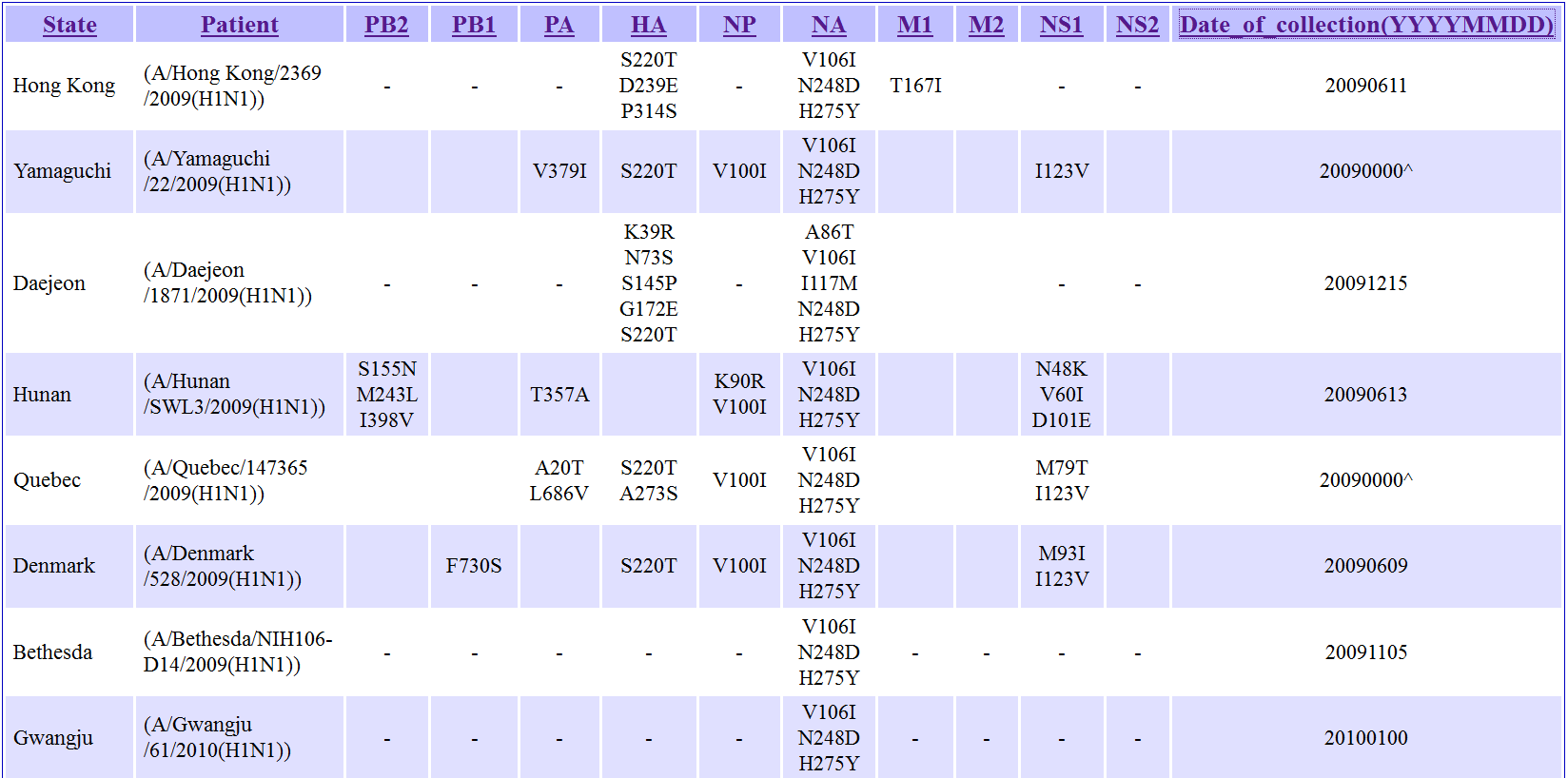
This table summarizes all the other mutations for viral samples that co-occurs with the current mutation-of-interest. Boxes with "-" means that sequence information for the gene is not available. Empty boxes means that no mutations were detected in the gene. Back to Summary of Mutation Back to Top 8) MUTATION: Literature that described about the mutation or its equivalent site The following will be displayed when user click on the hyperlink describing about the effects of the mutation occurring in an equivalent position in the Summary of Mutation page. 
This page describes the effect of mutation(s) occurring at an equivalent position of the mutation in the query based on curated information from literature. User may follow the hyperlink to view the reference in greater detail. Back to Summary of Mutation Back to Top 9) MUTATION: Structural view of mutation and its interactions with ligands The following will be displayed when user click on the hyperlink describing about the structural interactions the equivalent position of the mutation has in the Summary of Mutation page. 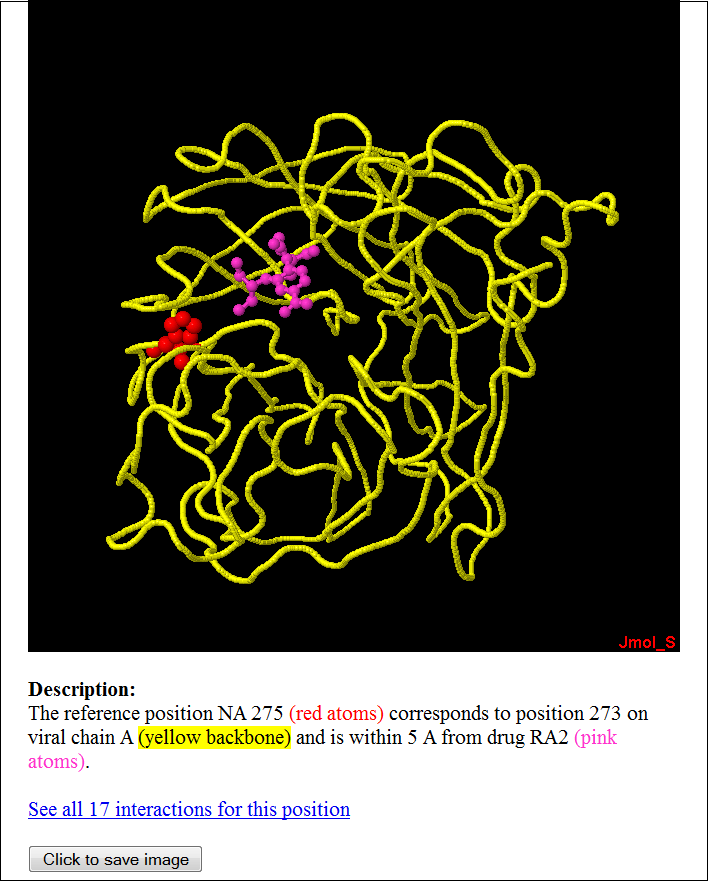
The mutated residue and the ligand are highlighted in different colors in the jmol applet. User can right-click on the applet to use jmol's functions to further examine the protein-ligand interactions in the structure. Back to Summary of Mutation Back to Top 10) MUTATION: Table of structures from Protein Data Bank showing ligand interacting at site of mutation The following will be displayed when user click on the "See all interactions at this position" hyperlink in the Summary of Mutation page. 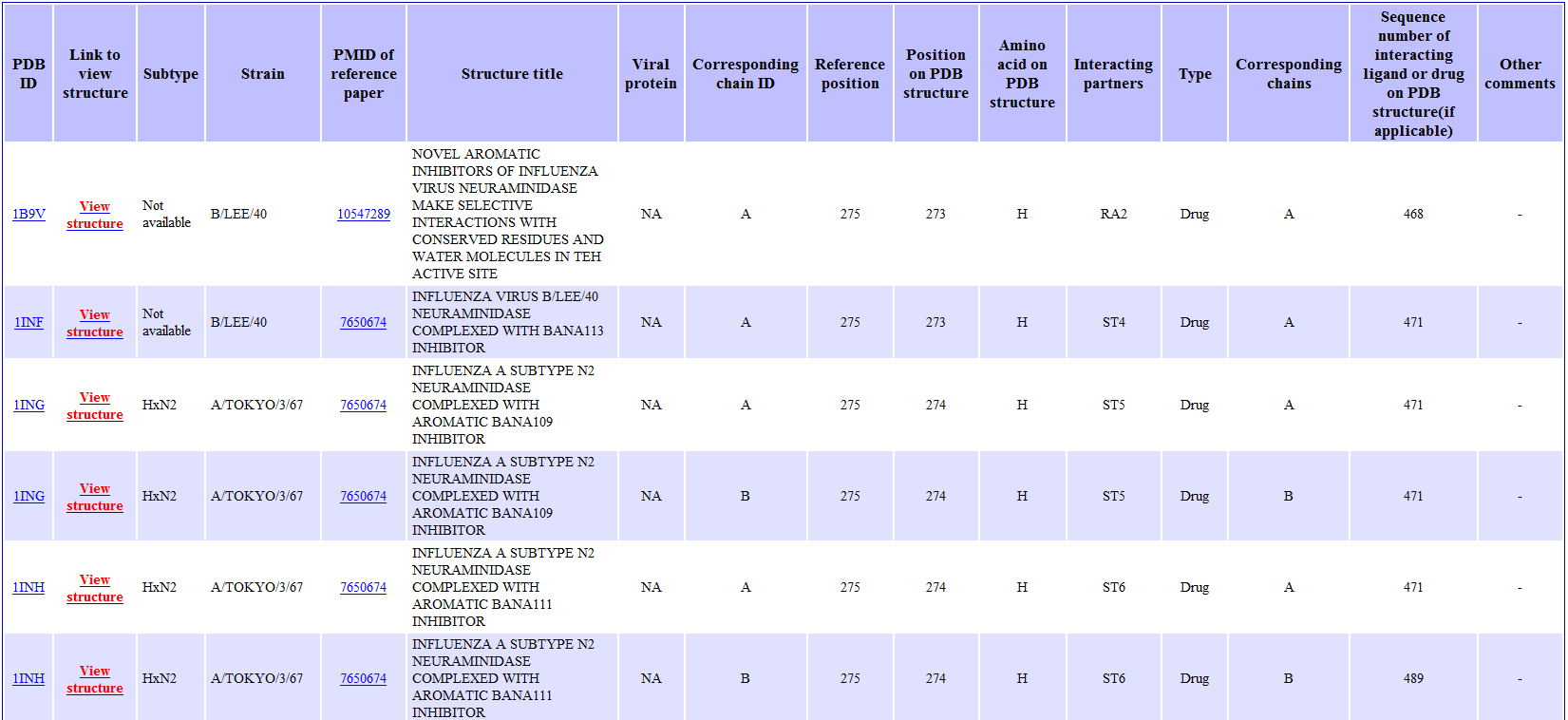
Back to Summary of Mutation Back to Top 11) RESULT: STRUCTURAL VIEW OF MUTATIONS The following will be displayed when user click on the "show in structure" hyperlink in the Result Summary page. 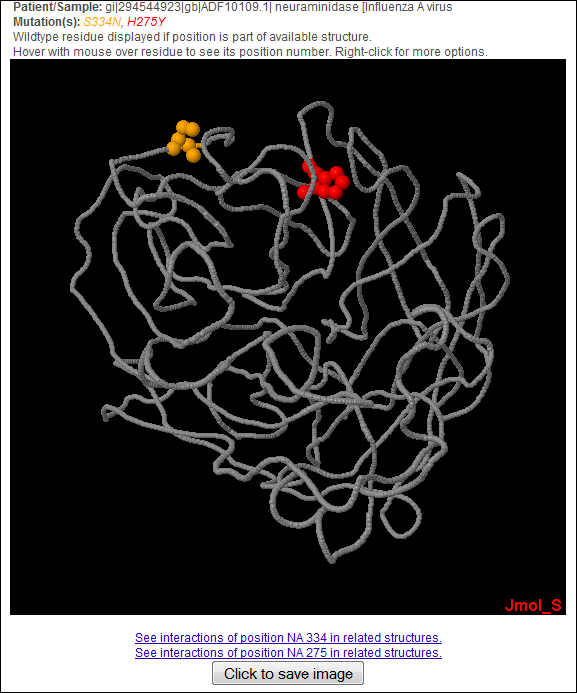
All mutations found in the query sequence are highlighted in this jmol applet. User can right-click on the applet to use jmol's functions to further examine the mutations in the protein structure. Back to Result Summary Back to Top 12) RESULT: TABLE SUMMARY OF MUTATIONS The following can be displayed when user click on the "Right-click here to save/download mutation report table for archiving or import to Excel" hyperlink in the Result Summary page. 
The "Warnlevel (0-3)" column indicates various degree of significance the mutation may have as detailed in section 2. Back to Result Summary Back to Top |
|
| |
|
|